AI is an essential technology for healthcare companies. In the pharma and medical devices industry, AI rapidly accelerates drug discovery and manufacturing and enables supply chain efficiencies. For healthcare payors and providers, AI tackles staff and skill shortages and increases administrative efficiency.
Although AI capabilities are still in their early stages, it has already begun revolutionizing the drug discovery process by streamlining research and potentially reducing the time and cost required to bring new drugs to market, addressing a broad range of unmet needs. AI also shows great promise in medical diagnostics, enhancing surgical precision, speeding up image analysis, and improving disease diagnosis.
Automation of routine tasks by AI can allow healthcare providers to see more patients, while personalized care, predictive analytics, and faster diagnoses can lead to better patient outcomes and a more positive patient experience.
Developing accurate AI models requires access to extensive, high-quality patient data from diverse populations. The use of healthcare data for AI development raises significant privacy concerns for both organizations and individuals. For instance, employing large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT to improve access to health information could impact patient privacy. Therefore, developing new data-sharing regulations and methods that preserve privacy is essential for the widespread adoption of AI applications in healthcare.
How medical device companies should approach AI investment
The matrix below details the areas of AI in which medical device companies should focus their time and resources. They should invest in the technologies shaded green, explore the prospect of investing in the technologies shaded yellow, and ignore the technologies shaded red.
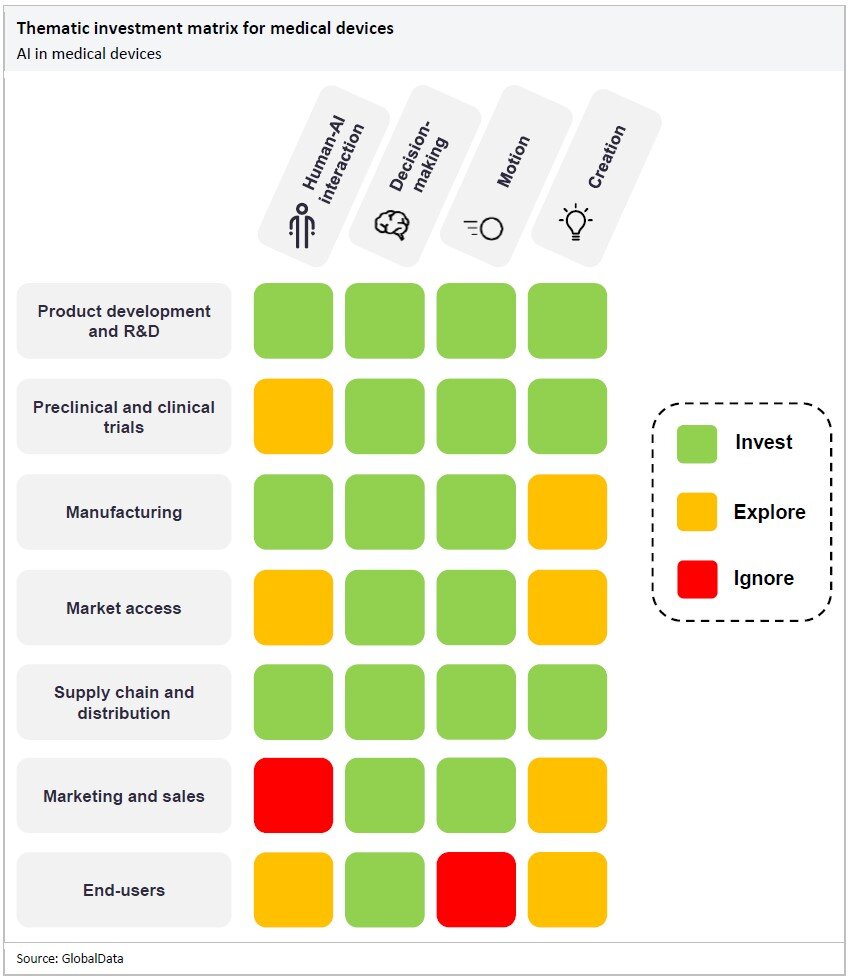
Medical device companies’ investment in AI should not be too dissimilar to that of pharma companies, as the industry is also under pressure to innovate. For manufacturing, AI can assist in quality control to ensure new products are fit for regulatory compliance. AI-enabled equipment can inspect products during the manufacturing process for defects, alert manufacturers of repeated defects, and find the cause of errors. Using AI to automate and complete quality-control checks for medical devices can also help increase the production line’s efficiency over time.
How AI helps tackle the challenge of medical imaging and diagnosis
Medical imaging is an essential tool to support disease diagnosis and treatment. The increasing use of medical imaging and the adoption of advanced technologies have resulted in additional burdens for radiologists. Without help from technologies such as AI, radiologists are tasked with manually checking large volumes of images. As a result, radiologists may be unable to devote sufficient time to each case, leading to errors and delays in diagnosis for patients.
Disparities in imaging access significantly impact patient outcomes. The availability of imaging services can be limited, especially for populations living in low-income countries. Some hospitals may not be able to afford newer high-tech imaging modalities. Low-resolution images decrease the accuracy of the assessment of medical conditions, and the outcome of a patient may be affected by the general imaging expertise of the institution.
Radiologists and pathologists routinely evaluate thousands of medical images to identify and diagnose diseases. However, inaccurate diagnoses due to human error or subjective interpretation may impact patient outcomes, especially if the radiologist is overburdened with work.
AI can assist in medical imaging analysis by viewing these medical images, saving radiologists valuable time. AI can distinguish abnormalities from normal findings by detecting minor image alterations, even spotting unseen abnormalities that the human eye cannot identify. AI can also improve the imaging of low-quality scans. Low-quality images greatly reduce the patient’s standard of care by leading to repeat scans, prolonged time to analyze and establish a diagnosis, and increased cost of care. Improving imaging quality gives healthcare professionals a clearer view of the patient’s pathology and reduces inequalities caused by the disparity of imaging equipment among hospitals and locations.
Researchers at the MIT Jameel Clinic have developed a new AI tool, Sybil, to predict the risk of a patient developing lung cancer within six years. Sybil analyzes low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans of lungs, currently the most common screening method for lung cancer. The study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, demonstrated that Sybil predicted cancer within one year with an average of 91% accuracy (between three datasets) and 79% accuracy within six years (Mikhael et al., 2023). Although still in its early stages, this example demonstrates the potential of AI-assisted predictive analysis of diseases.
AI-assisted medical imaging has the potential to revolutionize cancer detection and characterization. For example, experts at the Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, the Institute of Cancer Research, London, and Imperial College London developed an AI tool in 2023 to detect whether an abnormal growth in a CT scan is cancerous. Their study in April 2023 showed that their AI model could identify high-risk individuals for 82% of growths that were later found to be cancerous.
This technique can derive important information from CT scans that are invisible to the human eye. This AI model could speed up cancer diagnosis and treatment, which is significant because the earlier cancer is detected, the easier it is to cure. Initial studies show good results, but more tests must be done before these types of tools can be implemented into healthcare systems.
How AI helps tackle the challenge of administrative efficacy
The ability to make quick and purposeful decisions has traditionally been a differentiating factor for healthcare systems. Healthcare systems are focusing on speeding up and streamlining administrative decision-making and reducing overheads. Furthermore, maintaining appropriate staffing levels is a priority for healthcare systems. However, they face challenges due to higher turnover rates and increased competition for healthcare employees.
There is a shortage of talent across various job classifications, including medical staff, nursing, technology, support services, and administration. Additionally, wage inflation makes it harder to attract and retain good employees. Many healthcare practices are already operating at full capacity, making it difficult for staff to assist patients and complete administrative tasks comprehensively.
The ability to make quick and purposeful decisions has traditionally been a differentiating factor for healthcare systems. Healthcare systems are focusing on speeding up and streamlining administrative decision-making and reducing overheads. Furthermore, maintaining appropriate staffing levels is a priority for healthcare systems.
However, they face challenges due to higher turnover rates and increased competition for healthcare employees. There is a shortage of talent across various job classifications, including medical staff, nursing, technology, support services, and administration. Additionally, wage inflation makes it harder to attract and retain good employees. Many healthcare practices are already operating at full capacity, making it difficult for staff to assist patients and complete administrative tasks comprehensively.
However, implementing AI in healthcare administration creates challenges and limitations. AI is imperfect and can make errors; there may be questions about accountability and responsibility in the case of negative outcomes. The full-scale implementation of AI in healthcare administration will require rigorous testing and validation. Healthcare professionals need to be able to rely on technology without needing continuous validation and checks. Testing and validation ensure that the AI tools are accurate, reliable, and safe to use in healthcare settings.
Further, the implementation of AI in healthcare administration, while offering benefits such as faster healthcare delivery and mitigation of staff shortages, may have a damaging effect on doctor-patient relationships. Patients have expressed concerns about the lack of in-person interaction and the potential for increased medical errors when AI is used in clinical practice. Building trust and maintaining a strong doctor-patient relationship is crucial in healthcare, and the introduction of AI may raise concerns about the quality and personalization of care.
GlobalData, the leading provider of industry intelligence, provided the underlying data, research, and analysis used to produce this article.
GlobalData’s Thematic Intelligence uses proprietary data, research, and analysis to provide a forward-looking perspective on the key themes that will shape the future of the world’s largest industries and the organisations within them.