COMPANY
INSIGHT
Miniature Cable & Connectors for rapidly evolving medical instrument markets.
Advanced device technologies and medical sciences are evolving quickly and offering a wide range of new patient services to make our world a healthier place. Robotic assisted surgery offers micro-precision, while medical field effect sensors and bio-detectors provide the surgeon with improved patient monitoring information.
Magnetic proximity sensors
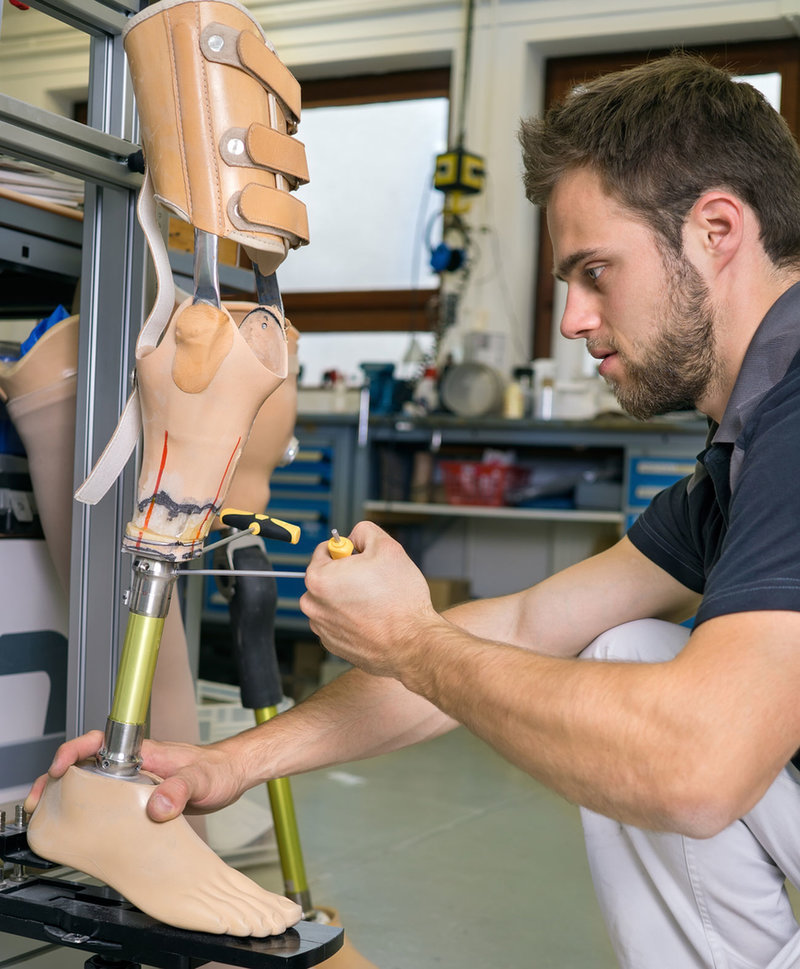
Newly wired magnetic proximity sensors give position and depth assistance when working with internal organ replacements. Perfusion sensing catheters can be used to monitor the patient’s blood flow into the brain and announce changes during the operation. Beyond the surgery room, changes are occurring in biosensor device designs from passive to active elements that can be attached to the body. With the combined assistance of mechanical and electrical engineering teams, we are seeing highly functioning prosthetic devices that nearly mimic our natural limbs. Some of the key elements to many of these technologies are the partnership of electronic sensors, electro-magnetic drives or motors, and miniaturized connection systems.
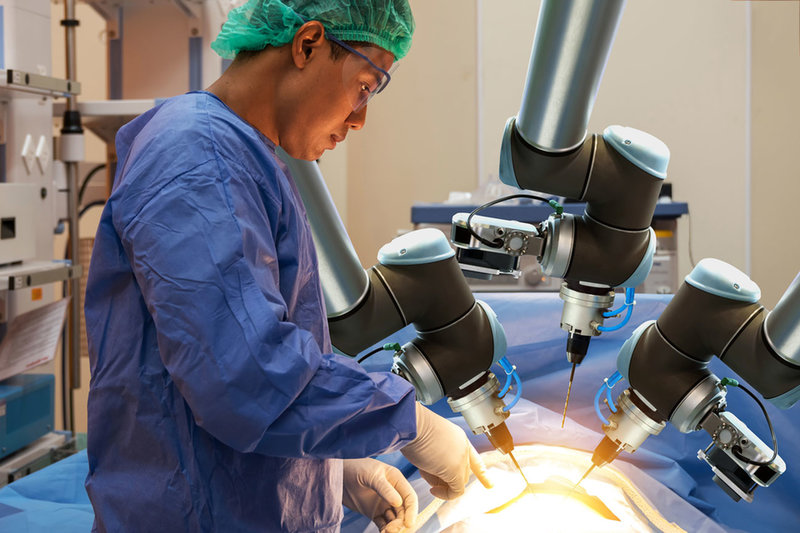
Medical cables
Specialized medical cables in newer medical devices are often smaller in diameter and more flexible because the chip technology runs on very low voltages and uses little current to operate. Connectors in medical equipment are also frequently smaller, lighter, and more rugged because of where they are being used. Chip sensors and processors have been moved from operating inside large instruments to nearer the action. Medical robotic devices are often positioned at EOA (end-of-arm) where the chip can process minute signals received from probes, transducers, and image detectors. The connectors in those places handle very low signals, even when carrying them short distances. Connectors and sensors support the use of frequently changed replacement tips as the robotic devices are used.

Medical technology evolution
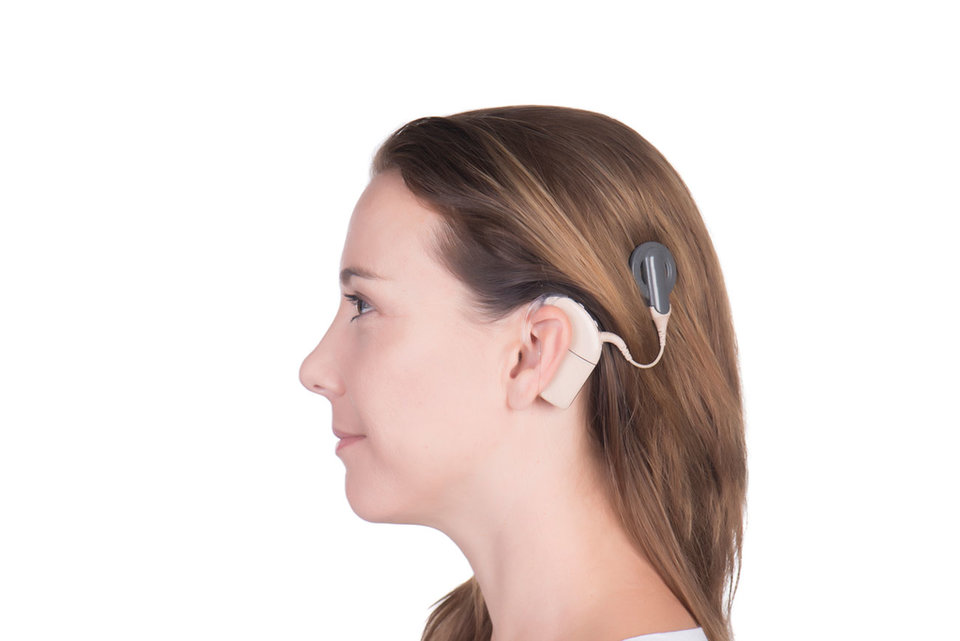
Connecting the brain to other parts of the body is the next challenge in medical technology evolution. For example, spinal stenosis in the lower vertebrae: a monitor and support device are connected to implanted catheters installed near the spine and worn continuously. Medical grade cable and connectors become critical—they must support the function, work comfortably, and survive the daily rigors of human life. Implantable epilepsy treatment devices must meet similar needs. Connectors and wiring materials are being specially designed for these advanced medical applications. Cochlear hearing device wiring at Omnetics Connector Corporation is very small but extremely rugged. High quality jacket insulation must withstand temperature and environmental changes, be resistant to humidity and ultraviolet degradation, and survive extensive daily use and abuse.

Connectors
Connectors are sometimes designed specifically for a medical device, process, or application. Connector manufacturers have solid modeling software technology that reduces time and cost significantly compared to previous practices. Medical equipment designers can select from a family of current standard devices and adjust them to size, shape, and pin count to meet their requirements. Automated machining or 3-d modeling further enhances the opportunity to get application-specific cables and connectors rapidly.
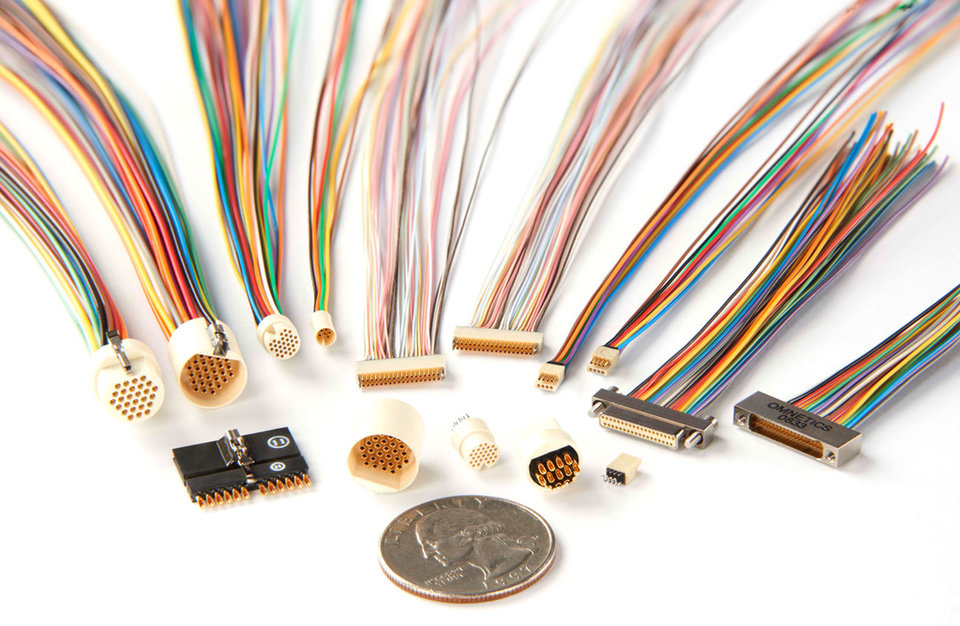

Nano-sized
Note the “Nano-sized” connectors that are often used in medical device electronics. Circular elements are often built into probe and catheter control handles at the end of a cable or within a control module, such as pain modulation devices. Reliability is often the key element in connector selection. To ensure highest signal integrity during mechanical shock and day-to-day vibration, designers should look carefully how the connector mates and stays mated. Most reliable connector designs use the “spring pin to solid socket” method. The connecting pins are made of tempered Beryllium Copper and are plated first with a nickel barrier and then over-plated with over 50 micro-inches of gold. The plated pins are designed to provide long wear without signal interruption and survive shock and vibration during use. The best materials that meet medical applications are stocked and have been tested by cable and connector suppliers. During new circuit prototype design, the product designer should select a connector that is similar to what they need. This allows them to proceed on the electrical circuit configuration during the short fabrication cycle of any application-specific design.
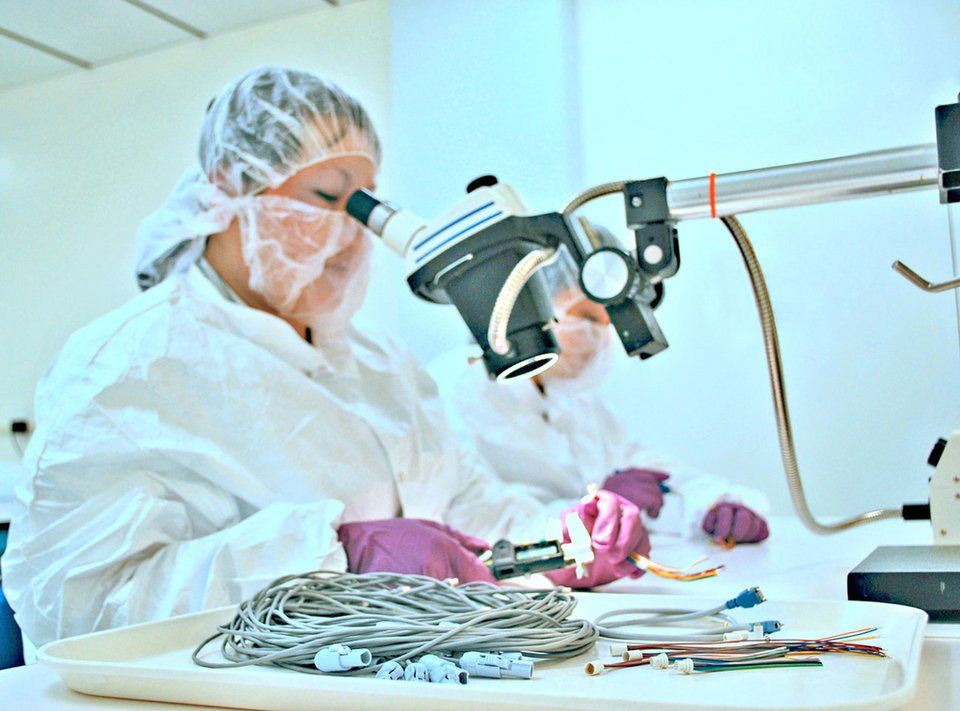

Omnetics is a connector company heavily involved in medical device design and supports many medical instrument companies. Omentics is a privately held, world class connector design and manufacturing company with over 35 years of experience focused upon a wide range of Micro and Nano miniature high reliability electronic connectors and interconnection systems. This includes standard and COTS connectors as well as the popular mixed power and signal connector systems.
Applied Harmonics:
All of Omnetics’ products are designed and assembled at our plant in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Processing equipment includes in-house automatic machining and over-molding equipment, wire crimping systems, and vapor-flow SMT soldering equipment. Omnetics’ proprietary spring-socket system passes the tests specified in Mil-83513 for micro connectors and is QPL status on the new Mil-32139 level program. This allows Omnetics to be a premier supplier in industry applications such as Military, Aerospace, Medical, Instrumentation.